Nose Experts
Rhinology and Sinus Diseases
Sinuses exist to humidify, purify and warm air. Sinuses also help make the head lighter and can provide a crumple zone in case of injury.
An average of 1-2 liters of mucus flows through the sinuses each day. This can increase due to allergies, infection, air pollution or smoke.
Sinuses work best when the air is warm, moist, oxygen rich and alkaline. Sinuses are challenged when the air is dry or smokey. Anatomy, swelling, infection, allergic reaction, and foreign objects can also affect sinuses negatively.
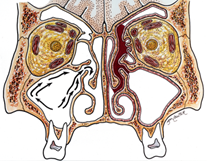
The anatomy of an individual’s sinuses can also cause problems with sinuses. These can include a deviated septum, nasal polyps, concha bullosa, and haller cells.
The types of infection most common with sinuses can include acute/subacute rhinosinusitis, chronic rhinosiusitis, and fungus balls.
Treatment of sinus problems
The goal of sinus treatment is to restore proper drainage of sinuses, remove any diseased tissues, restore aeration and re-establish normal airflow dynamics.
The types of treatment options available include environmental controls, medications, immunotherapy (allergy injections), surgery and/or a combination of these.
Sinus medications can include saline rinse, antihistamines, decongestants, steroids, antibiotics, and leukotriene antagonists.
Surgical Treatment Options
- Inferior Turbinate Reduction – Used to open the narrowest part of the nose and is performed in the office with only local anesthesia.
- Septoplasty – Outpatient surgery performed through a small incision inside the nose to straighten the bone and cartilage dividing the two nostrils (septum).
- Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS) – A minimally invasive outpatient procedure to establish natural drainage of sinuses.
- Sinus Surgery – Used to opens sinuses in a systematic, graduated approach using image guidance. This outpatient surgery is performed through the nose with endoscopes (no incisions) to restore function and reduce turbinates.
- Balloon Sinuplasty – Used to re-establishes natural drainage of sinuses, this ultra-minimally invasive office procedure is performed with local anesthesia.
