Our Otology experts specialize in treating all types of ear diseases and disorders including, but not limited to:
Treatment techniques can include medical, surgical and technological options. Our physicians and audiologists also specialize in bone anchored, cochlear and other types of implantable hearing devices.
What Causes Hearing Loss?
A variety of hearing problems affect over a third of people over sixty. These include:
Sensorineural hearing (high frequency) loss due to damage to the inner ear or nerve pathways caused by illness, medications, hereditary or genetic issues, trauma, malformation of the inner ear, exposure to loud noise or simply aging.
Conductive hearing loss due to difficulty in the external or middle ear caused by ear infections, fluid buildup, perforated eardrum, benign tumors, abnormal bone growth, or impacted earwax.
Mixed hearing loss – a combination of conductive and sensorineural loss.
Treatment Options
Hearing loss often steadily worsens if left untreated. Treatments can include medical, surgical and technological options. Our physicians and audiologists will work together to determine the most effective treatment option for you.
Cochlear Implant
A cochlear implant is a small, complex electronic device that helps provide a sense of sound to individuals who are hearing impaired beyond the help of a hearing aid. While hearing aids amplify sound, cochlear implants compensate for damaged parts of the inner ear. An implant does not restore normal hearing, but it can provide an auditory understanding of the environment and speech.
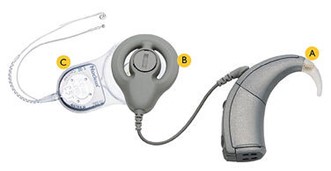
Who benefits from cochlear implants?
Baha Implants
Bone anchored hearing aids are surgically implanted prosthetic devices that use your body’s own natural ability to conduct sound by bypassing the damaged outer and middle ear, and sending the sound directly to your healthy inner ear through an implanted magnetic bone conduction system.
Who can benefit from Baha Systems?
Commonly called “glaucoma of the inner ear,” Meniere’s disease is related to the inner ear in which the balance system is housed.
For those with Meniere’s disease, the fluids which enable a person to keep their balance and maintain normal hearing, are over-abundant causing the patient to experience severe spinning, vertigo, nausea, hearing loss, tinnitus, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. As the disease progresses, hearing loss becomes progressively worse and attacks become unpredictable.
Treatment options include:
Recent statistics show that more than 90 million Americans will experience dizziness at some time during their lives. But what is the difference between dizziness, vertigo and disequilibrium?
Dizziness is very general and describes a feeling of lightheadedness, faintness or giddiness. Near-faint dizziness, psychophysiologic dizziness, ocular dizziness and multisensory dizziness are all various types of dizziness disorders.
Vertigo is the illusion that either you or the environment around you is spinning, rotating, rolling, rocking, or whirling. In some cases, people experience the sensation of tilting.
Disequilibrium is the sensation of being unsteady or in a state of disequilibrium – imbalance occurs only when people are standing or walking.
Diagnosing patients with dizziness, vertigo or imbalance
Evaluation of medical history, a neurotologic examination and tests of hearing and balance function are the first steps. Testing for allergies, autoimmune inner ear disease or hormonal imbalance may also be necessary. Imaging studies with a CT or MRI and a consultation with neurologist or cardiologist could be indicated. Once a diagnosis has been made a plan of treatment can be established.
Causes can include:
Treatment Plans can include:
Tinnitus is the perception of sound in the head or ears when no external sound is present. It is often described as “ringing in the ears”, but can also take the form of hissing, clicking, roaring or other similar sounds.
The American Tinnitus Association estimates that more than 50 million Americans experience tinnitus to some degree. For most, tinnitus is diagnosed as a benign, chronic condition that requires no treatment. Others find it a plaguing affliction that cannot be ignored and can be so debilitating that it impacts all aspects of life.
Tinnitus is most commonly caused by hearing loss and exposure to loud noise including exposure to guns firing, rock concerts, chain saws, and other loud noises. Occasionally side effects from medications, drugs or alcohol can also cause tinnitus.
Individuals with tinnitus should be evaluated by an ENT physician to rule out any serious problem that may be treated.
The diagnosis of chronic otitis media (infection of the middle ear), includes any disease affecting the eardrum or the three small ear bones and may cause a conductive hearing loss by interfering with the transmission of sound to the inner ear. When an acute infection develops in the middle ear, the eardrum may rupture, resulting in a perforation.
Many procedures are now being performed as an outpatient ambulatory surgery in the physician’s office. The use of surgical lasers allows pinpoint accuracy, instantaneous cauterization of bleeding vessels, and high energy cutting while minimizing trauma to the surrounding tissue.
The procedures performed include:
The facial nerve travels through the temporal bone, exits at the skull base, and passes through the parotid gland to innervate the muscles of the face. Disorders of the facial nerve cause different signs and symptoms such as facial paralysis, synkinesis, or hemifacial spasm.
Disorders of the facial nerve include:
Facial paralysis of any kind needs to be diagnosed promptly and correctly to maximize the chances of recovery. Treatment protocols can include medications, Botox, surgery, and physical therapy.
Audiologists perform all the hearing and inner ear testing for hearing loss, dizziness and balance problems. These tests give a complete picture of how the inner ear is functioning and provide information necessary to make an accurate diagnosis of hearing and balance/dizziness problems.
Audiological Assessment
The audiological assessment consists of a hearing test and immittance audiometry.
The hearing test is a subjective test performed to assess the function of the auditory system, the degree of hearing loss and a patient’s ability to discriminate speech.
Immittance audiometry is an objective test measuring the status of the middle ear and reflexes of the auditory muscle to determine whether there is fluid present and if the eardrum and bones of hearing are functioning normally.
Electronystagmography (ENG) (VNG)
This multi-part testing is used to determine problems within the vestibular (balance) portion of the inner ear by testing eye movements, positioning, and the function of each individual balance system.
Balance Testing (CDP) and Rotary Chair
A test of the vestibular (inner ear) system, it measures eye movements in response to a rotating chair eliciting the vestibulo-ocular response (VOR). It helps identify the source of dizziness and imbalance.
Balance Testing using the Balance Master
Balance testing using a computerized balance platform can assess the entire balance mechanism to determine where deficiencies may exist. Input from the eyes, the inner ear, and the proprioceptive system (nerve endings in the muscles and joints) is all tested on this equipment.
Brainstem auditory evoked response (BAER)
The Brainstem Auditory Evoked Response is an objective measure of the electrical activity of the auditory nerve pathway from the inner ear to the brainstem. The BAER is helpful in the diagnosis of a growth on the hearing nerve, demyelinating diseases (multiple sclerosis) of the brain, tumors (acoustic neuroma) of the eighth cranial nerve (hearing and balance nerve) and vascular lesions (strokes) of the brain stem. BAER testing can be used in place of a conventional hearing test for infants and other individuals as necessary.
Electrocochleography (ECoG)
ECoG is an objective test that determines the pressures within the inner ear which may indicate Meniere’s disease.
Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE)
This test is done to check the response of the outer hair cells in the cochlea. This test helps diagnose whether the pathology is in the hair cells or in the hearing nerve.
Under Florida law, e-mail addresses are public records. If you do not want your e-mail address released in response to a public records request, do not send electronic mail to this entity. Instead, contact First Physicians Group’s Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Center by phone or in writing:
OTOLARYNGOLOGY HEAD AND NECK CENTER:
1901 Floyd Street, Sarasota, FL 34239 | (941) 366-9222
WEBSITES:
First Physicians Group | Sarasota Memorial Health Care System
PRIVACY POLICY:
Please click here to read our Privacy Policy.
CONSUMER INFO:
Agency for Health Care Administration
Centers for Medicare / Medicaid Services